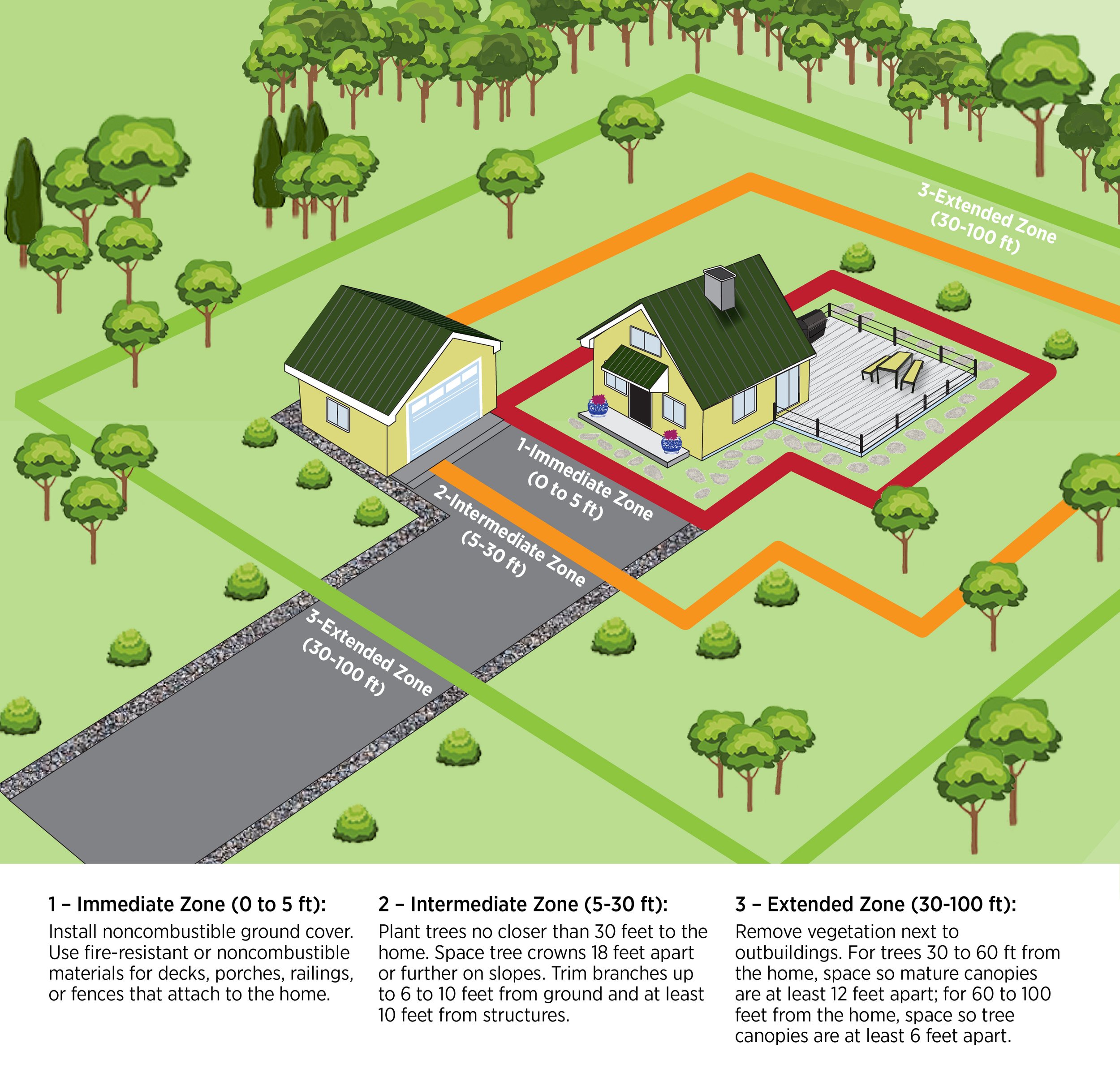
Defensible Space
Defensible space is the buffer between your home and the native vegetation surrounding it. Having defensible space acts as a fuel break that can keep your home safe from wildfire and is intended to slow the rate of spread and intensity of wildfire. Defensible space gives fire and emergency personal a safe area to work in to protect you and your home if a wildfire closes in. Having defensible space does not mean the entire area around your home has to be bare soil. There are lots of options for wildfire resistant landscapes that can help slow the spread of fire to your home. A fire-safe landscape and hardening your home could make all the difference in saving it. To be compliant with the state of California Public Resource Code (PRC) 4291, land owners are required to have a minimum of 100 feet of defensible space around buildings and structures. Starting January 1st, 2023, CALFIRE and the state of California will enforce the following defensible space zones. Each county may have different requirements, so be sure to check with your local enforcement agency.
Defensible Space Zones
*The following information, and more, can be found here on CALFIRE’s website.
Zone 1 - Ember Resistant Zone
Zone 1 extends 5 feet from buildings, structures, decks, etc.
The ember-resistant zone is currently not required by law, but science has proven it to be the most important of all the defensible space zones. This zone includes the area under and around all attached decks, and requires the most stringent wildfire fuel reduction. The ember-resistant zone is designed to keep fire or embers from igniting materials that can spread the fire to your home. The following provides guidance for this zone, which may change based on the regulation developed by the Board of Forestry and Fire Protection.
Use hardscape like gravel, pavers, concrete and other noncombustible mulch materials. No combustible bark or mulch
Remove all dead and dying weeds, grass, plants, shrubs, trees, branches and vegetative debris (leaves, needles, cones, bark, etc.); Check your roofs, gutters, decks, porches, stairways, etc.
Remove all branches within 10 feet of any chimney or stovepipe outlet
Limit plants in this area to low growing, nonwoody, properly maintained plants
Limit combustible items (outdoor furniture, planters, etc.) on top of decks
Relocate firewood and lumber to Zone 2
Replace combustible fencing, gates, and arbors attach to the home with noncombustible alternatives
Consider relocating garbage and recycling containers outside this zone
Consider relocating boats, RVs, vehicles and other combustible items outside this zone
Zone 2 – Lean, Clean and Green Zone
Zone 2 extends 30 feet from buildings, structures, decks, etc. or to your property line, whichever is closer.
Remove all dead plants, grass and weeds (vegetation).
Remove dead or dry leaves and pine needles from your yard, roof and rain gutters.
Remove branches that hang over your roof and keep dead branches 10 feet away from your chimney.
Trim trees regularly to keep branches a minimum of 10 feet from other trees.
Relocate wood piles to Zone 2.
Remove or prune flammable plants and shrubs near windows.
Remove vegetation and items that could catch fire from around and under decks, balconies and stairs.
Create a separation between trees, shrubs and items that could catch fire, such as patio furniture, wood piles, swing sets, etc.
*During times of drought when green landscaping cannot be achieved due to water restrictions be sure to remove all dead or dying material from Zone 1.
Zone 3 – Reduce Fuel Zone
Zone 3 extends from 30 feet to 100 feet out from buildings, structures, decks, etc. or to your property line, whichever is closer.
Cut or mow annual grass down to a maximum height of 4 inches.
Create horizontal space between shrubs and trees. (See diagram)
Create vertical space between grass, shrubs and trees. (See diagram)
Remove fallen leaves, needles, twigs, bark, cones, and small branches. However, they may be permitted to a depth of 3 inches.
All exposed wood piles must have a minimum of 10 feet of clearance, down to bare mineral soil, in all directions.